Understanding TLS Certificates: Why they matter for your Website
by Nico Kempe, Founder
Understanding TLS Certificates: Why they matter for your Website
When you’re managing a website, one of the most important aspects of security is protecting the data exchanged between your users and your server. That’s where TLS (Transport Layer Security) certificates come into play, ensuring that data remains encrypted and private. But why should you pay for a certificate when free alternatives like Let's Encrypt exist? Let’s break down what TLS certificates are, their types, and why paying for one might make sense for you.
What is a TLS Certificate?
A TLS certificate authenticates your website and encrypts the data transferred between your users and the server. Although commonly referred to as SSL certificates (after their predecessor), modern certificates use the more secure TLS protocol. In other words, when people talk about SSL certificates, they are actually (mostly) talking about TLS.
TLS vs. SSL: The Difference
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) was the original encryption protocol, but due to security vulnerabilities, it has been replaced by TLS. Although both terms are still used interchangeably, TLS is the current and secure standard, while SSL is deprecated.
Why Pay for a TLS Certificate?
-
Trust & Validation: Paid certificates provide additional layers of validation, such as Organization Validation (OV) or Extended Validation (EV), which showcase your organization’s legitimacy, enhancing user trust.
-
Warranty & Support: Many paid certificates come with warranties in case something goes wrong with the certificate. Additionally, customer support helps with installation, renewal, and troubleshooting—an advantage that free certificates lack.
-
Longer Validity: While Let’s Encrypt certificates are free, they currently require renewal every 90 days. Paid certificates can last up to two years, reducing the risk of expiration and potential downtime.
-
Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Google prioritizes secure websites in its search rankings. While both free and paid TLS certificates provide encryption, the added trust signals from OV or EV certificates can enhance your site's credibility. Furthermore, avoiding certificate expiration (which can happen more easily with short-term free certificates) ensures uninterrupted SEO benefits, helping your website rank better over time.
The Dangers of not using a valid TLS Certificate
If your website does not have a valid TLS certificate, visitors might encounter warnings like the one below:
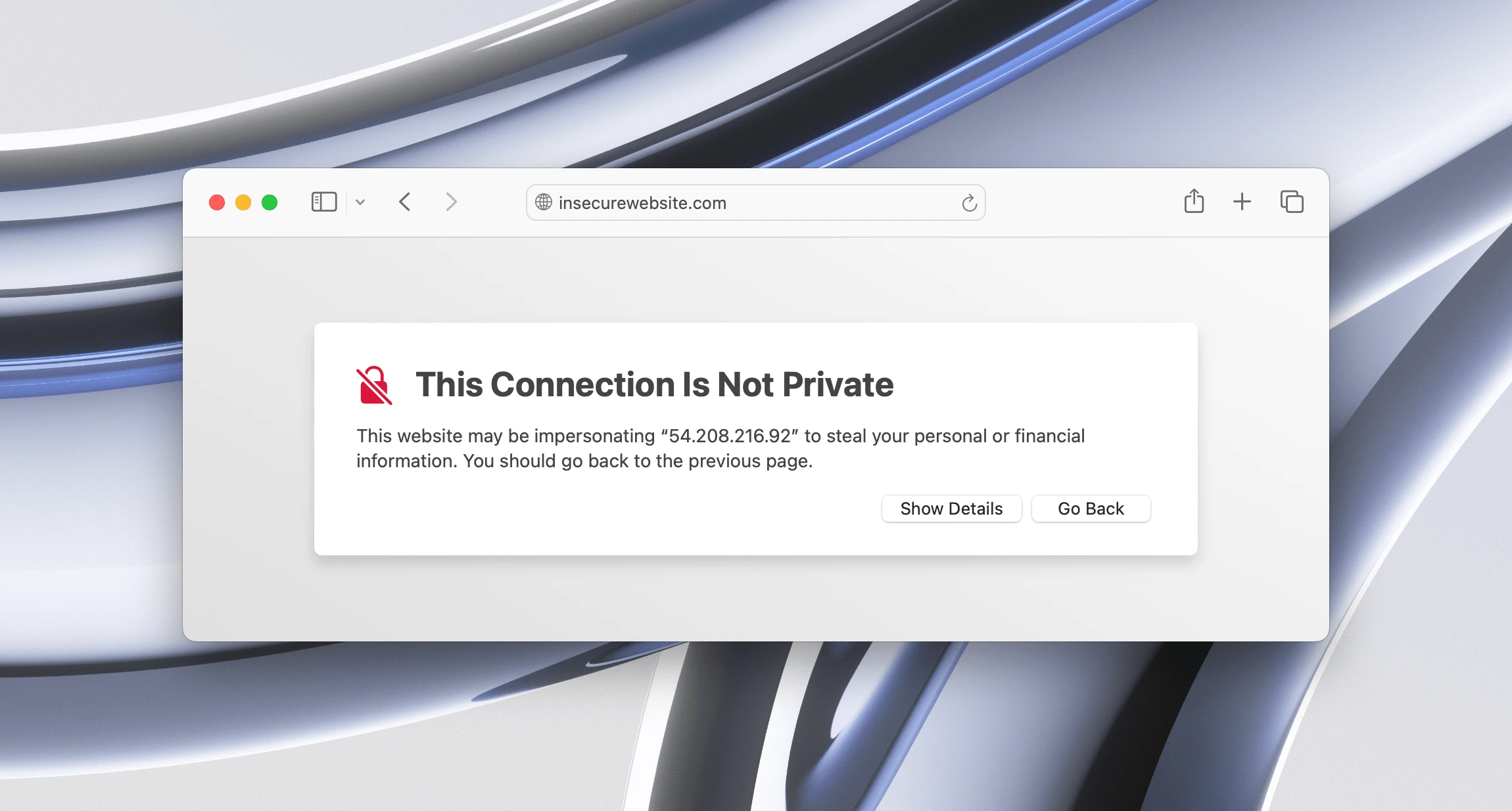
This warning indicates that the connection between the user and your website is not secure, potentially exposing personal or financial information to malicious attacks. Such messages can deter users from visiting your site, harming your reputation and causing you to lose potential customers. For businesses that handle sensitive data, these errors are not just inconveniences—they represent a significant security risk and a potential compliance issue.
Types of TLS Certificates
- Domain Validation (DV): Validates that the certificate holder controls the domain. It’s quick to obtain but doesn’t provide visible trust indicators.
- Organization Validation (OV): Offers additional validation, showing users that the website belongs to a legitimate organization.
- Extended Validation (EV): The highest level of validation that involves rigorous checks of the organization.
Note: Although EV certificates used to display the organization’s name directly in the browser’s address bar (often with a green bar), most modern browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge no longer show this visual distinction. Instead, the EV certificate details can be viewed by clicking on the padlock icon in the address bar. This change was made to simplify the user experience and focus more on secure connections (HTTPS) rather than visual indicators.
Other Security Certificates we offer
Beyond TLS certificates, we also offer a variety of other security certificates, each serving a unique purpose:
-
Code Signing Certificates: These certificates are used by developers to sign their software, ensuring that the code has not been tampered with since it was signed. This is crucial for maintaining trust and security in distributed software applications.
-
Document Signing Certificates: These are used to sign documents digitally, ensuring their authenticity and integrity. They are commonly used in legal, financial, and business settings where document authenticity is critical.
-
S/MIME Certificates: Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (S/MIME) certificates are used to encrypt and digitally sign emails, protecting your communications from unauthorized access and verifying the sender’s identity.
-
VMC (Verified Mark Certificates): VMCs allow your logo to appear next to your emails in supported email clients, adding brand recognition and authenticity to your communications. This feature helps combat phishing and increases trust with your audience.
Choosing the Right Certificate
With various options available, choosing the right certificate can be tricky. As a reseller of top Certificate Authorities like DigiCert, GeoTrust, GlobalSign, Sectigo, and Thawte through InterNetX, we can help you select the perfect certificate based on your specific needs.
Need Help?
If you're not sure which certificate is right for you, feel free to reach out via our contact page. We can guide you through the process and help you choose the best option to secure your website.